Alpha Selection
Regularization is designed to penalize model complexity, therefore the higher the alpha, the less complex the model, decreasing the error due to variance (overfit). Alphas that are too high on the other hand increase the error due to bias (underfit). It is important, therefore to choose an optimal alpha such that the error is minimized in both directions.
The AlphaSelection Visualizer demonstrates how different values of alpha influence model selection during the regularization of linear models. Generally speaking, alpha increases the affect of regularization, e.g. if alpha is zero there is no regularization and the higher the alpha, the more the regularization parameter influences the final model.
Visualizer |
|
Quick Method |
|
Models |
Regression |
Workflow |
Model selection, Hyperparameter tuning |
For Estimators with Built-in Cross-Validation
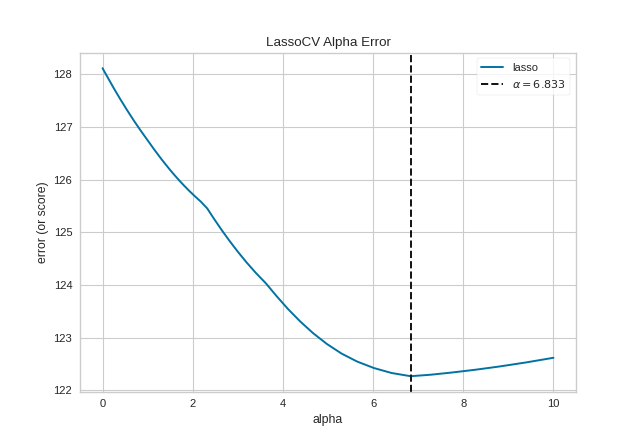
The AlphaSelection visualizer wraps a “RegressionCV” model and
visualizes the alpha/error curve. Use this visualization to detect if
the model is responding to regularization, e.g. as you increase or
decrease alpha, the model responds and error is decreased. If the
visualization shows a jagged or random plot, then potentially the model
is not sensitive to that type of regularization and another is required
(e.g. L1 or Lasso regularization).
Note
The AlphaSelection visualizer requires a “RegressorCV” model, e.g.
a specialized class that performs cross-validated alpha-selection
on behalf of the model. See the ManualAlphaSelection visualizer if
your regression model does not include cross-validation.
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LassoCV
from yellowbrick.datasets import load_concrete
from yellowbrick.regressor import AlphaSelection
# Load the regression dataset
X, y = load_concrete()
# Create a list of alphas to cross-validate against
alphas = np.logspace(-10, 1, 400)
# Instantiate the linear model and visualizer
model = LassoCV(alphas=alphas)
visualizer = AlphaSelection(model)
visualizer.fit(X, y)
visualizer.show()
(Source code, png, pdf)
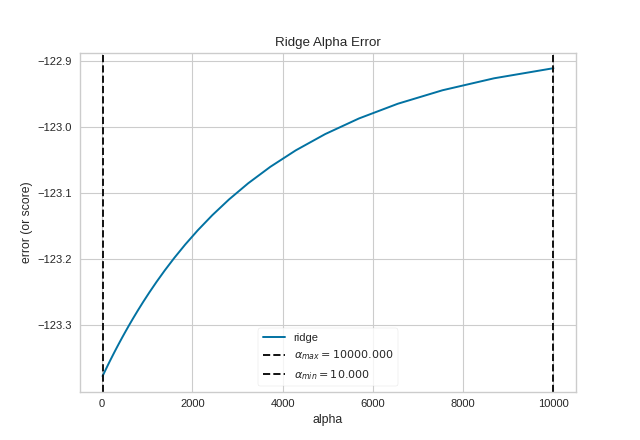
For Estimators without Built-in Cross-Validation
Most scikit-learn Estimators with alpha parameters
have a version with built-in cross-validation. However, if the
regressor you wish to use doesn’t have an associated “CV” estimator,
or for some reason you would like to specify more control over the
alpha selection process, then you can use the ManualAlphaSelection
visualizer. This visualizer is essentially a wrapper for scikit-learn’s
cross_val_score method, fitting a model for each alpha specified.
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
from yellowbrick.datasets import load_concrete
from yellowbrick.regressor import ManualAlphaSelection
# Load the regression dataset
X, y = load_concrete()
# Create a list of alphas to cross-validate against
alphas = np.logspace(1, 4, 50)
# Instantiate the visualizer
visualizer = ManualAlphaSelection(
Ridge(),
alphas=alphas,
cv=12,
scoring="neg_mean_squared_error"
)
visualizer.fit(X, y)
visualizer.show()
(Source code, png, pdf)
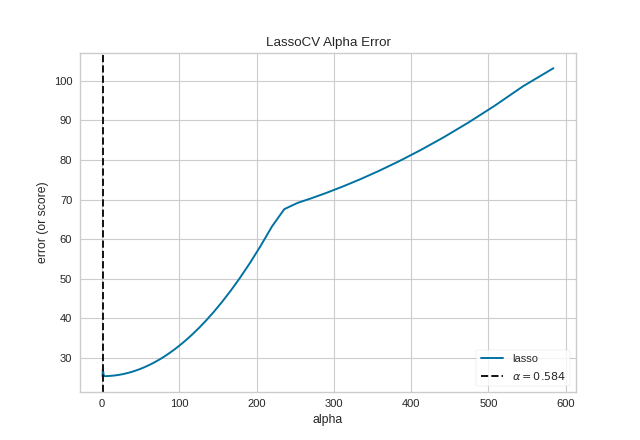
Quick Methods
The same functionality above can be achieved with the associated quick method alphas. This method will build the AlphaSelection Visualizer object with the associated arguments, fit it, then (optionally) immediately show it.
from sklearn.linear_model import LassoCV
from yellowbrick.regressor.alphas import alphas
from yellowbrick.datasets import load_energy
# Load dataset
X, y = load_energy()
# Use the quick method and immediately show the figure
alphas(LassoCV(random_state=0), X, y)
(Source code, png, pdf)
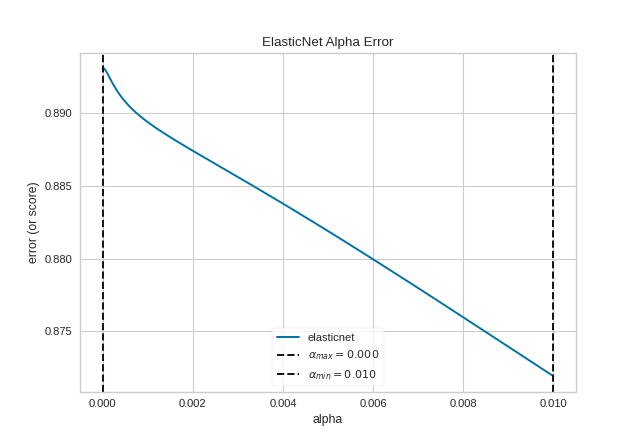
The ManualAlphaSelection visualizer can also be used as a oneliner:
from sklearn.linear_model import ElasticNet
from yellowbrick.regressor.alphas import manual_alphas
from yellowbrick.datasets import load_energy
# Load dataset
X, y = load_energy()
# Instantiate a model
model = ElasticNet(tol=0.01, max_iter=10000)
# Use the quick method and immediately show the figure
manual_alphas(model, X, y, cv=6)
(Source code, png, pdf)
API Reference
Implements alpha selection visualizers for regularization
- class yellowbrick.regressor.alphas.AlphaSelection(estimator, ax=None, is_fitted='auto', **kwargs)[source]
Bases:
RegressionScoreVisualizerThe Alpha Selection Visualizer demonstrates how different values of alpha influence model selection during the regularization of linear models. Generally speaking, alpha increases the affect of regularization, e.g. if alpha is zero there is no regularization and the higher the alpha, the more the regularization parameter influences the final model.
Regularization is designed to penalize model complexity, therefore the higher the alpha, the less complex the model, decreasing the error due to variance (overfit). Alphas that are too high on the other hand increase the error due to bias (underfit). It is important, therefore to choose an optimal Alpha such that the error is minimized in both directions.
To do this, typically you would you use one of the “RegressionCV” models in Scikit-Learn. E.g. instead of using the
Ridge(L2) regularizer, you can useRidgeCVand pass a list of alphas, which will be selected based on the cross-validation score of each alpha. This visualizer wraps a “RegressionCV” model and visualizes the alpha/error curve. Use this visualization to detect if the model is responding to regularization, e.g. as you increase or decrease alpha, the model responds and error is decreased. If the visualization shows a jagged or random plot, then potentially the model is not sensitive to that type of regularization and another is required (e.g. L1 orLassoregularization).- Parameters
- estimatora Scikit-Learn regressor
Should be an instance of a regressor, and specifically one whose name ends with “CV” otherwise a will raise a YellowbrickTypeError exception on instantiation. To use non-CV regressors see:
ManualAlphaSelection. If the estimator is not fitted, it is fit when the visualizer is fitted, unless otherwise specified byis_fitted.- axmatplotlib Axes, default: None
The axes to plot the figure on. If None is passed in the current axes will be used (or generated if required).
- is_fittedbool or str, default=’auto’
Specify if the wrapped estimator is already fitted. If False, the estimator will be fit when the visualizer is fit, otherwise, the estimator will not be modified. If ‘auto’ (default), a helper method will check if the estimator is fitted before fitting it again.
- kwargsdict
Keyword arguments that are passed to the base class and may influence the visualization as defined in other Visualizers.
Notes
This class expects an estimator whose name ends with “CV”. If you wish to use some other estimator, please see the
ManualAlphaSelectionVisualizer for manually iterating through all alphas and selecting the best one.This Visualizer hooks into the Scikit-Learn API during
fit(). In order to pass a fitted model to the Visualizer, call thedraw()method directly after instantiating the visualizer with the fitted model.Note, each “RegressorCV” module has many different methods for storing alphas and error. This visualizer attempts to get them all and is known to work for RidgeCV, LassoCV, LassoLarsCV, and ElasticNetCV. If your favorite regularization method doesn’t work, please submit a bug report.
For RidgeCV, make sure
store_cv_values=True.Examples
>>> from yellowbrick.regressor import AlphaSelection >>> from sklearn.linear_model import LassoCV >>> model = AlphaSelection(LassoCV()) >>> model.fit(X, y) >>> model.show()
- class yellowbrick.regressor.alphas.ManualAlphaSelection(estimator, ax=None, alphas=None, cv=None, scoring=None, **kwargs)[source]
Bases:
AlphaSelectionThe
AlphaSelectionvisualizer requires a “RegressorCV”, that is a specialized class that performs cross-validated alpha-selection on behalf of the model. If the regressor you wish to use doesn’t have an associated “CV” estimator, or for some reason you would like to specify more control over the alpha selection process, then you can use this manual alpha selection visualizer, which is essentially a wrapper forcross_val_score, fitting a model for each alpha specified.- Parameters
- estimatoran unfitted Scikit-Learn regressor
Should be an instance of an unfitted regressor, and specifically one whose name doesn’t end with “CV”. The regressor must support a call to
set_params(alpha=alpha)and be fit multiple times. If the regressor name ends with “CV” aYellowbrickValueErroris raised.- axmatplotlib Axes, default: None
The axes to plot the figure on. If None is passed in the current axes will be used (or generated if required).
- alphasndarray or Series, default: np.logspace(-10, 2, 200)
An array of alphas to fit each model with
- cvint, cross-validation generator or an iterable, optional
Determines the cross-validation splitting strategy. Possible inputs for cv are:
None, to use the default 3-fold cross validation,
integer, to specify the number of folds in a (Stratified)KFold,
An object to be used as a cross-validation generator.
An iterable yielding train, test splits.
This argument is passed to the
sklearn.model_selection.cross_val_scoremethod to produce the cross validated score for each alpha.- scoringstring, callable or None, optional, default: None
A string (see model evaluation documentation) or a scorer callable object / function with signature
scorer(estimator, X, y).This argument is passed to the
sklearn.model_selection.cross_val_scoremethod to produce the cross validated score for each alpha.- kwargsdict
Keyword arguments that are passed to the base class and may influence the visualization as defined in other Visualizers.
Notes
This class does not take advantage of estimator-specific searching and is therefore less optimal and more time consuming than the regular “RegressorCV” estimators.
Examples
>>> from yellowbrick.regressor import ManualAlphaSelection >>> from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge >>> model = ManualAlphaSelection( ... Ridge(), cv=12, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error' ... ) ... >>> model.fit(X, y) >>> model.show()
- draw()[source]
Draws the alphas values against their associated error in a similar fashion to the AlphaSelection visualizer.
- fit(X, y, **args)[source]
The fit method is the primary entry point for the manual alpha selection visualizer. It sets the alpha param for each alpha in the alphas list on the wrapped estimator, then scores the model using the passed in X and y data set. Those scores are then aggregated and drawn using matplotlib.
- yellowbrick.regressor.alphas.alphas(estimator, X, y=None, ax=None, is_fitted='auto', show=True, **kwargs)[source]
Quick Method: The Alpha Selection Visualizer demonstrates how different values of alpha influence model selection during the regularization of linear models. Generally speaking, alpha increases the affect of regularization, e.g. if alpha is zero there is no regularization and the higher the alpha, the more the regularization parameter influences the final model.
- Parameters
- estimatora Scikit-Learn regressor
Should be an instance of a regressor, and specifically one whose name ends with “CV” otherwise a will raise a YellowbrickTypeError exception on instantiation. To use non-CV regressors see:
ManualAlphaSelection. If the estimator is not fitted, it is fit when the visualizer is fitted, unless otherwise specified byis_fitted.- Xndarray or DataFrame of shape n x m
A matrix of n instances with m features.
- yndarray or Series of length n
An array or series of target values.
- axmatplotlib Axes, default: None
The axes to plot the figure on. If None is passed in the current axes will be used (or generated if required).
- is_fittedbool or str, default=’auto’
Specify if the wrapped estimator is already fitted. If False, the estimator will be fit when the visualizer is fit, otherwise, the estimator will not be modified. If ‘auto’ (default), a helper method will check if the estimator is fitted before fitting it again.
- showbool, default: True
If True, calls
show(), which in turn callsplt.show()however you cannot callplt.savefigfrom this signature, norclear_figure. If False, simply callsfinalize()- kwargsdict
Keyword arguments that are passed to the base class and may influence the visualization as defined in other Visualizers.
- Returns
- visualizerAlphaSelection
Returns the alpha selection visualizer
- yellowbrick.regressor.alphas.manual_alphas(estimator, X, y=None, ax=None, alphas=None, cv=None, scoring=None, show=True, **kwargs)[source]
Quick Method: The Manual Alpha Selection Visualizer demonstrates how different values of alpha influence model selection during the regularization of linear models. Generally speaking, alpha increases the affect of regularization, e.g. if alpha is zero there is no regularization and the higher the alpha, the more the regularization parameter influences the final model.
- Parameters
- estimatoran unfitted Scikit-Learn regressor
Should be an instance of an unfitted regressor, and specifically one whose name doesn’t end with “CV”. The regressor must support a call to
set_params(alpha=alpha)and be fit multiple times. If the regressor name ends with “CV” aYellowbrickValueErroris raised.- axmatplotlib Axes, default: None
The axes to plot the figure on. If None is passed in the current axes will be used (or generated if required).
- alphasndarray or Series, default: np.logspace(-10, 2, 200)
An array of alphas to fit each model with
- cvint, cross-validation generator or an iterable, optional
Determines the cross-validation splitting strategy. Possible inputs for cv are:
None, to use the default 3-fold cross validation,
integer, to specify the number of folds in a (Stratified)KFold,
An object to be used as a cross-validation generator.
An iterable yielding train, test splits.
This argument is passed to the
sklearn.model_selection.cross_val_scoremethod to produce the cross validated score for each alpha.- scoringstring, callable or None, optional, default: None
A string (see model evaluation documentation) or a scorer callable object / function with signature
scorer(estimator, X, y).This argument is passed to the
sklearn.model_selection.cross_val_scoremethod to produce the cross validated score for each alpha.- kwargsdict
Keyword arguments that are passed to the base class and may influence the visualization as defined in other Visualizers.
- Returns
- visualizerAlphaSelection
Returns the alpha selection visualizer